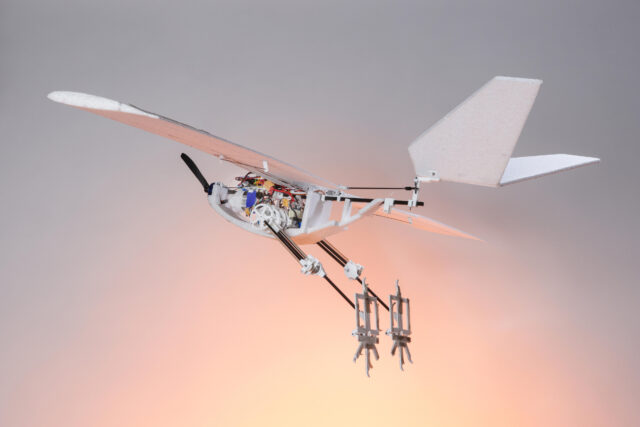
Most drones on the market are rotary-wing quadcopters, which can conveniently land and take off almost anywhere. The problem is they are less energy-efficient than fixed-wing aircraft, which can fly greater distances and stay airborne for longer but need a runway, a dedicated launcher, or at least a good old-fashioned throw to get to the skies.
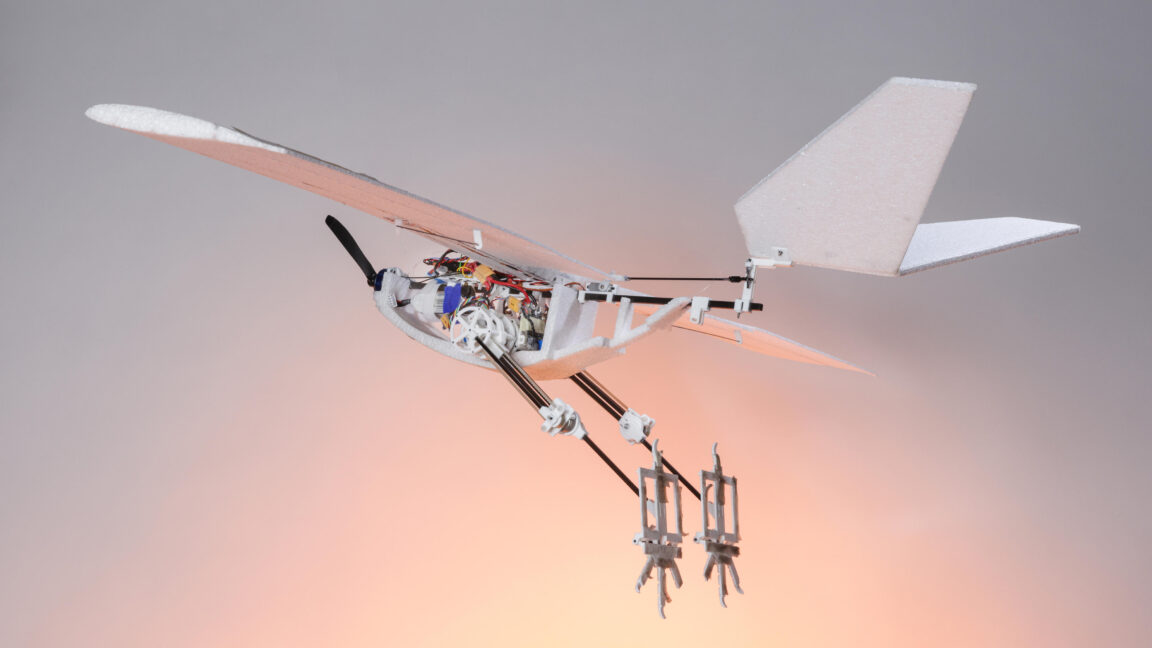
To get past this limit, a team of Swiss researchers at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne built a fixed-wing flying robot called RAVEN (Robotic Avian-inspired Vehicle for multiple ENvironments) with a peculiar bio-inspired landing gear: a pair of robotic bird-like legs. “The RAVEN robot can walk, hop over obstacles, and do a jumping takeoff like real birds,” says Won Dong Shin, an engineer leading the project.
Smart investments
The key challenge in attaching legs to drones was that they significantly increased mass and complexity. State-of-the-art robotic legs were designed for robots walking on the ground and were too bulky and heavy to even think about using on a flying machine. So, Shin’s team started their work by taking a closer look at what the leg mass budget looked like in various species of birds.
It turned out that the ratio of leg mass to the total body weight generally increased with size in birds. A carrion crow had legs weighing around 100 grams, which the team took as their point of reference.
The robotic legs built by Shin and his colleagues resembled a real bird’s legs quite closely. Simplifications introduced to save weight included skipping the knee joint and actuated toe joints, resulting in a two-segmented limb with 64 percent of the weight placed around the hip joint. The mechanism was powered by a standard drone propeller, with the ankle joint actuated through a system of pulleys and a timing belt. The robotic leg ended with a foot with three forward-facing toes and a single backward-facing hallux.


 Loading comments...
Loading comments...
