QLED TV manufacturers have dug themselves into a hole.
After years of companies promising that their quantum dot light-emitting diode TVs use quantum dots (QDs) to boost color, some industry watchers and consumers have recently started questioning whether QLED TVs use QDs at all. Lawsuits have been filed, accusing companies like TCL of using misleading language about whether their QLED TVs actually use QDs.
In this article, we'll break down why new conspiracy theories about QLED TVs are probably overblown. We'll also explore why misleading marketing from TV brands is responsible for customer doubt and how it all sets a bad precedent for the future of high-end displays, including OLED TVs and monitors.
What QLED TVs are supposed to do
TVs that use QDs are supposed to offer wider color gamuts and improved brightness over their QD-less LCD-LED counterparts. Just ask Samsung, which says that QLED displays deliver “a wider range of colors,” “better color coverage,” and “a brighter picture.” TCL will tell you that its QLED TVs use “billions of Quantum Dot nanocrystals” and deliver “industry-leading color palette and brightness.”
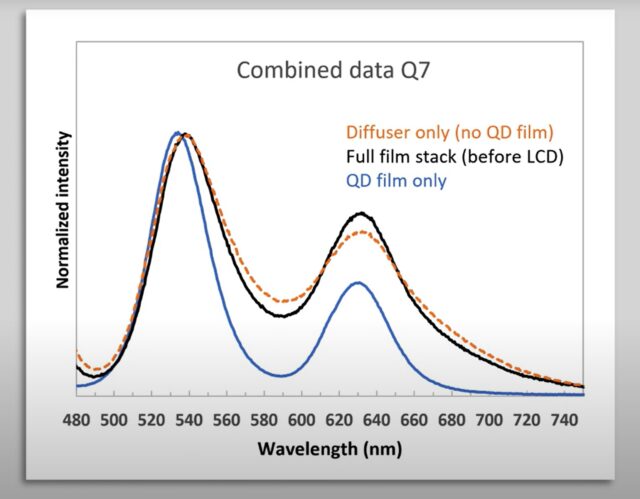
To be clear, properly manufactured QD TVs that use a sufficient quantity of QDs are legit. Excellent examples, which command higher prices than QD-free rivals, successfully deliver bright pictures with wide color gamuts and impressive color volume (the number of colors a TV displays at various levels of brightness). A TV with strong color volume can depict many light and dark shades of green, for example.
Technology reviews site RTINGS, which is known for its in-depth display testing, explains that a TV with good color volume makes "content look more realistic," while "TVs with poor color volume don't show as many details." This is QLED's big selling point. A proper QLED TV can be brighter than an OLED TV and have markedly better color volume than some high-end, non-QD LCD-LED displays.


 Loading comments...
Loading comments...
